Chemistry and Materials Earth Sciences and Environment Engineering and Energy Fundamental physics Mathematics and Computer Science Medicine and Life Sciences All High Performance Algorithms for the Computation of the Hardy Function - Dissemination & Development
ARCHER2-eCSE11-07 : Dr David M Lewis (University of Liverpool)Subject Area:
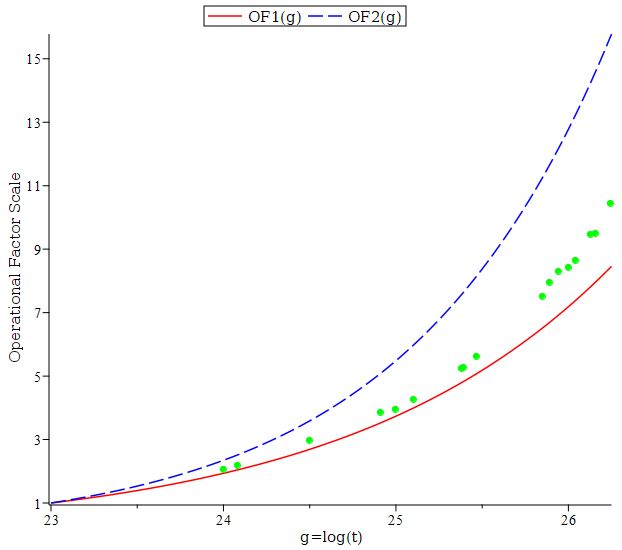
Mathematics and Computer Science The Riemann zeta-function is of fundamental interest in a number of areas of mathematical research, including number theory, theoretical physics, random matrix theory and cryptography. Hardy’s Z-function – defined by Z(t)=eIθ(t) ζ(1⁄2+it) for θ(t)∈ℝ – plays an important role in the theory of the Riemann zeta-function ζ(s) for s∈ℂ and its deep connection to the distribution of prime numbers. In recent years, the PI of this eCSE project discovered a theoretical formulation of the Hardy Z-function in terms of generalised Gauss sums. The asymptotic characteristics of the parameters governing these sums raised the prospect of potential new algorithms for the rapid evaluation of Z(t), using a novel recursive methodology. The aim of this eCSE project was to bring these proposed new algorithms into reality, by developing new, faster, open access Z(t) computational codes and make them available for general use via an open-access repository. The new source codes developed during the project show considerable speed-up compared to what was previously available, which should be of considerable interest to the mathematical research community and make an impact on practical applications of these fields to the public sphere. Read more...
Scalable and robust Firedrake deployment on ARCHER2 and beyond
ARCHER2-eCSE04-05 : Dr David A Ham (Imperial College London)Subject Area:
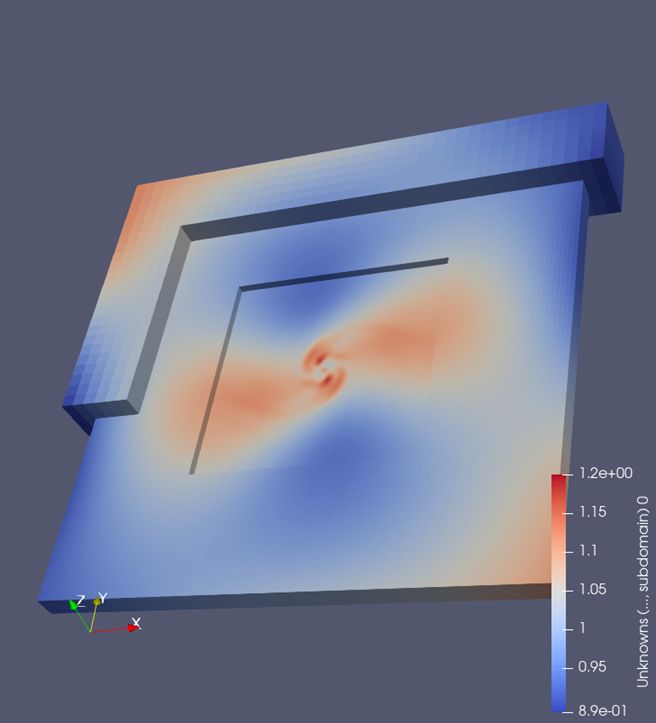
Mathematics and Computer Science This project aimed to standardise and simplify the build procedure for Firedrake, a system for solving partial differential equations. Previously, expert HPC knowledge and significant time investment were required to carry out bespoke installation on HPC systems. Using Spack, a package manager specifically designed for installing popular software on HPC systems, a package was created which allows a non-expert user to quickly install Firedrake on an HPC system in a single line, saving a huge amount of time. Further Spack packages were also created for other applications that themselves depend on Firedrake, including applications for modelling weather, coastal ocean zones and glacier flow. Read more...
Upscaling ExaHyPE
ARCHER2-eCSE04-02 : Dr Tobias Weinzierl (University of Durham)Subject Area:
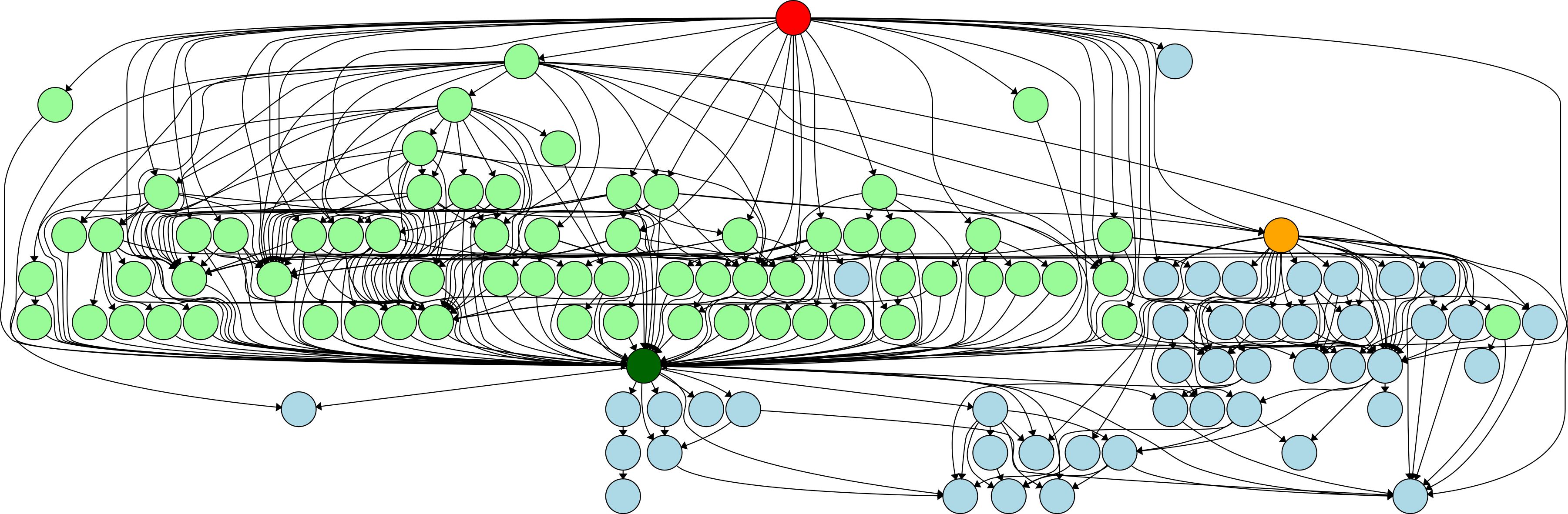
Mathematics and Computer Science ExaHyPE is an open-source simulation engine which is used for astrophysical challenges and seismic problems such as earthquake simulation. It hides most of the computing aspects from users, who need only enter the relevant scientific parameters when creating a new simulation code. This means a new simulation can be prepared in just a few hours, whereas it could take weeks, months, or even years to write from scratch. ExaHyPE is also designed to be able to exploit the future generation of exascale computers, which will have many more cores per node than current supercomputers. The need to harvest these cores makes task-based programming increasingly attractive. However, introducing tasks into codes also introduces other complexities. This eCSE project carried out modifications which have allowed the ExaHyPE code to run astrophysical simulations with unprecedented compute efficiency. As electricity costs rise and concerns grow over the environmental impact of supercomputing, there is an ever-growing focus on the need to increase the efficiency of simulation codes. Read more...
Scalable I/O and checkpointing for Firedrake
ARCHER2-eCSE01-20 : Dr David A Ham (Imperial College London)Subject Area:
Mathematics and Computer Science Firedrake is an automated system for the solution of partial differential equations using the finite element method (FEM). This project improved the input/output capability of Firedrake for the running and analysis of simulations such as geophysical fluid dynamics. Other applications of Firedrake include coastal ocean simulations, weather forecasting, and marine renewable energy supply. This project also extended the HDF5 interface of the Portable, Extensible Toolkit for Scientific Computation (PETSc). Read more...