Implementing a multiphase flow modelling capability targeting boiling in the high-fidelity software CHAPSim2
ARCHER2-eCSE08-06
PI: Dr Wei Wang (STFC Daresbury Laboratory)
Co-I(s): Dr Charles Moulinec (STFC Daresbury Laboratory), Dr Marco Colombo (University of Sheffield)
Technical staff: Dr Bo Liu (STFC Daresbury Laboratory))
Subject Area:
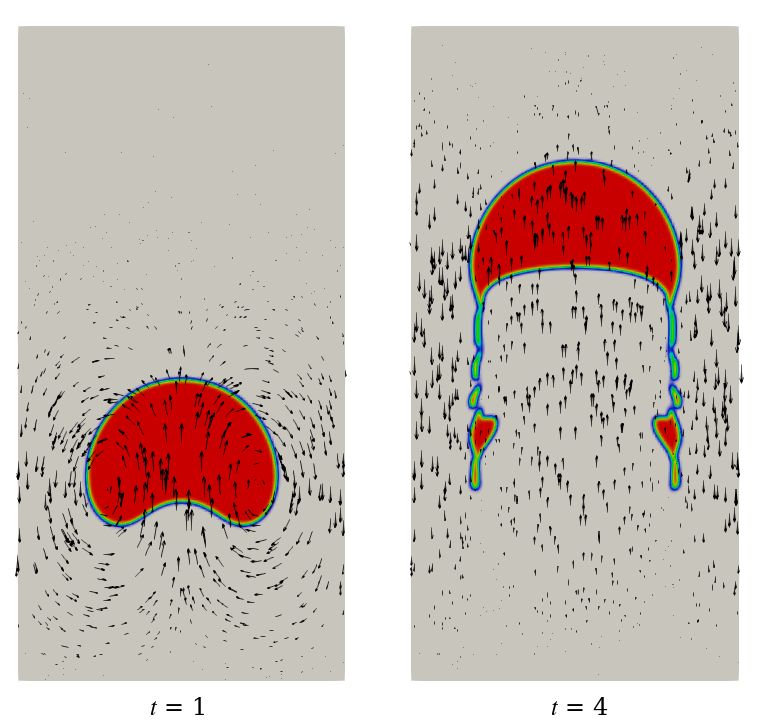
Dynamics of a Rising Bubble Modelled with CHAPSim2
The development of a robust multiphase flow solver in CHAPSim2 is motivated by the growing need for high-fidelity simulations of boiling and related phenomena, which play a critical role in industrial and energy applications. Improved modelling of boiling processes, particularly in nuclear reactors, could lead to more accurate predictions of the critical heat flux that governs safe operating margins. Reducing conservatism in these limits is of considerable economic value, as it allows for lower construction cost and therefore more efficient power generation. Outside the nuclear sector, accurate multiphase capabilities also enhance understanding and design of systems in chemical and process engineering and other fields where bubbling processes may have a significantly impact.
This project extends CHAPSim2, a high-order Direct Numerical Simulation (DNS) software originally designed for single-phase flows, by integrating an advanced Volume of Fluid (VOF) method and an advanced Multi-dimensional Tangent of Hyperbola Interface Capturing (MTHINC) algorithm. Instead of relying on geometric reconstructions of the interface, the MTHINC scheme employs algebraic approximations of the phase boundary, preserving a sharp interface and reducing numerical issues. This new module has been coupled with CHAPSim2’s existing high-order flow solver, thereby enhancing both accuracy and consistency in the solution of the momentum and phase transport equations. Benchmark studies, including rotating disk/sphere problem and rising bubble tests, in 2-D and 3-D, have demonstrated the software’s ability in predicting interface evolution, bubble rising velocity, and deformation in line with reference or benchmark data. Scalability tests on ARCHER2 show overall good parallel performance of the software, although functions accounting for communication across processors remain a target for further optimisation.
CHAPSim2 is a highly scalable, high-accuracy, and high-fidelity DNS solver, capable of delivering detailed and precise turbulence and heat transfer simulations. The newly added VOF module inherits the underlying numerical infrastructure of CHAPSim2, leveraging its high-order schemes and partitioning strategy to simulate complex multiphase phenomena without sacrificing performance. This lays the foundation for future developments aimed at modelling boiling flows and assessing heat transfer mechanisms with greater fidelity, ultimately contributing to safer and more effective industrial and energy systems.
Information about the code
CHAPSim2 is available from github
Following this eCSE project, a new “two-phase” branch has been added to the CHAPSim2 source code for the two-phase functionality.